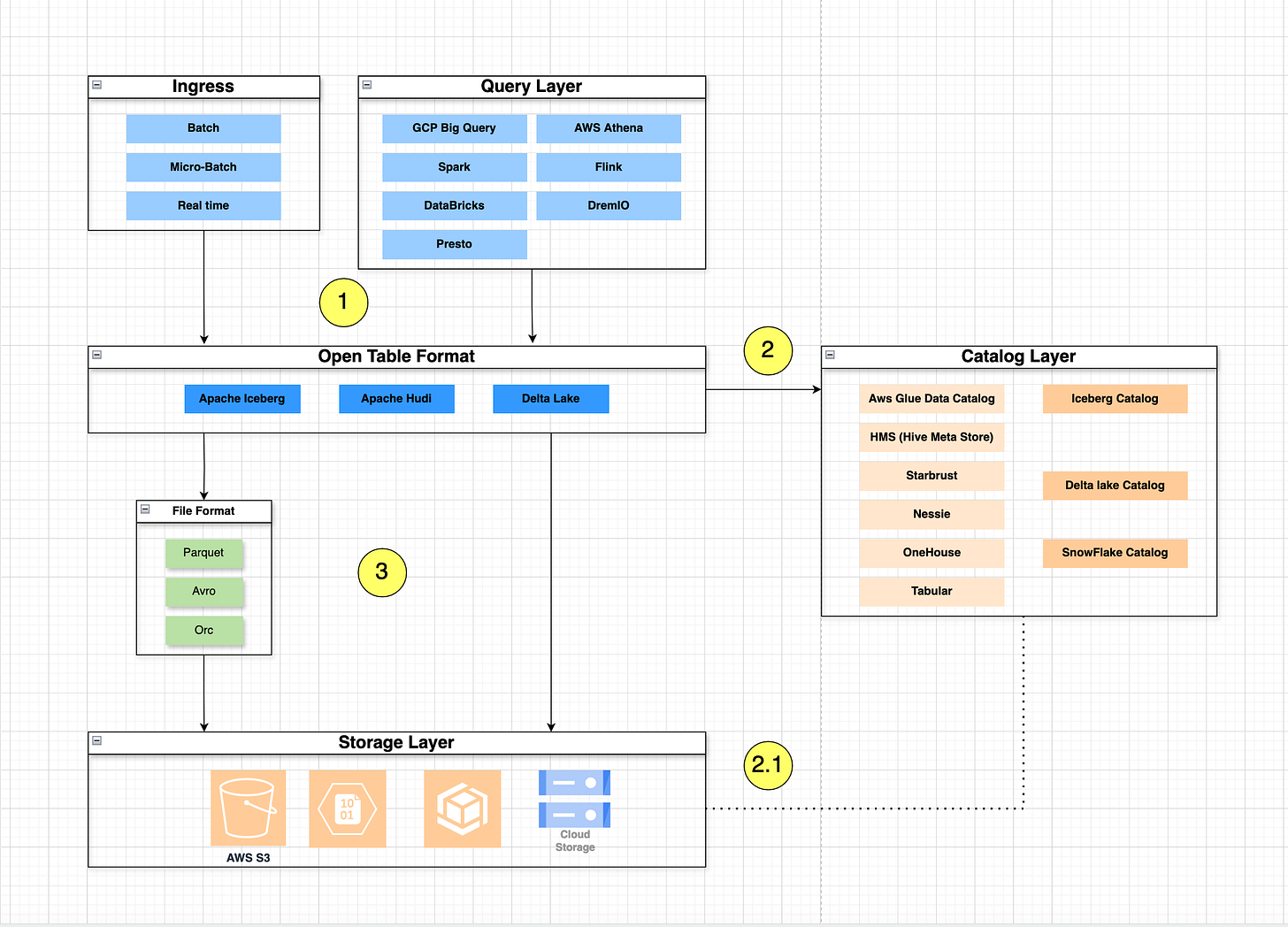
Open table Format for Transactional DataLake
Data Warehouse to Data Lake/Lakehouse ?
Traditionally, data warehouses have been chosen for their capacity to store and process large data volumes. However, they come with limitation such as high costs, limited scalability, and rigid governance.
There has been a significant shift in the data landscape towards data lakes and lakehouses as viable alternatives to traditional or cloud-native data warehouses. Lakehouses, in particular, offer a more flexible and scalable architecture capable of handling both structured and unstructured data. A key technology driving this evolution is the open data table format.
Open Table Format
The open table format organizes and manages data in a data lake efficiently, supporting both data warehousing (query) and data science workloads (processing). It promotes improved interoperability, comparable performance, and enhanced governance and transactional support.
Organizes data into structured tables within distributed storage systems (e.g., HDFS, S3).
Supports schema evolution without downtime or complex migrations.
Provides ACID transactions for maintaining data consistency and reliability.
Allows time travel by querying historical snapshots of data.
Efficiently handles incremental data changes with support for batch and near-real-time processing.
Uses columnar file formats (e.g., Parquet) and metadata to track changes over time.
Optimizes data access and performance through partitioning and indexing.
Main Technologies for Open Data Tables
Several technologies play crucial roles in open data tables:
Apache Iceberg: A flexible and scalable open table format for organizing and managing data in a data lake, used by engines for storage and query operations.
Delta Lake: Built on Apache Spark, it provides robust and scalable data management capabilities in a data lake, extending support through dataframe and dataset APIs.
Apache Hudi: Designed for real-time analytics on streaming data, offering efficient data management in a data lake with the HoodiDataSet API.
Conclusion
Adopting open data tables facilitates the transition from a traditional data warehouse to a lakehouse architecture, enhancing interoperability, performance, governance, and flexibility. Organizations can leverage the combined benefits of data warehouses and data lakes, including improved scalability, enhanced or same performance, and robust governance at lower cost.